ad
Overview
In my previous post, I built a local PC transcription app using Whisper. This time, we’ll add speaker separation (diarization). Instead of real names, the audio will be split into speakers like Speaker A, B, C, and each segment will include a timeline. This is handy for meeting minutes or when creating subtitles.
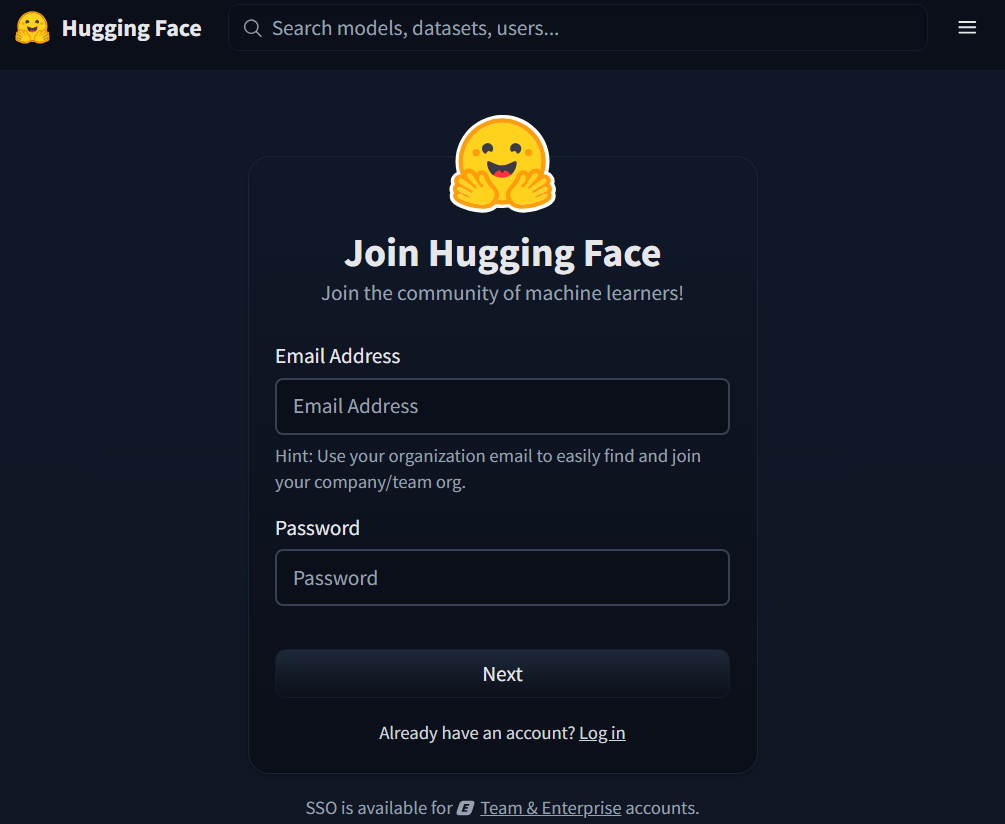
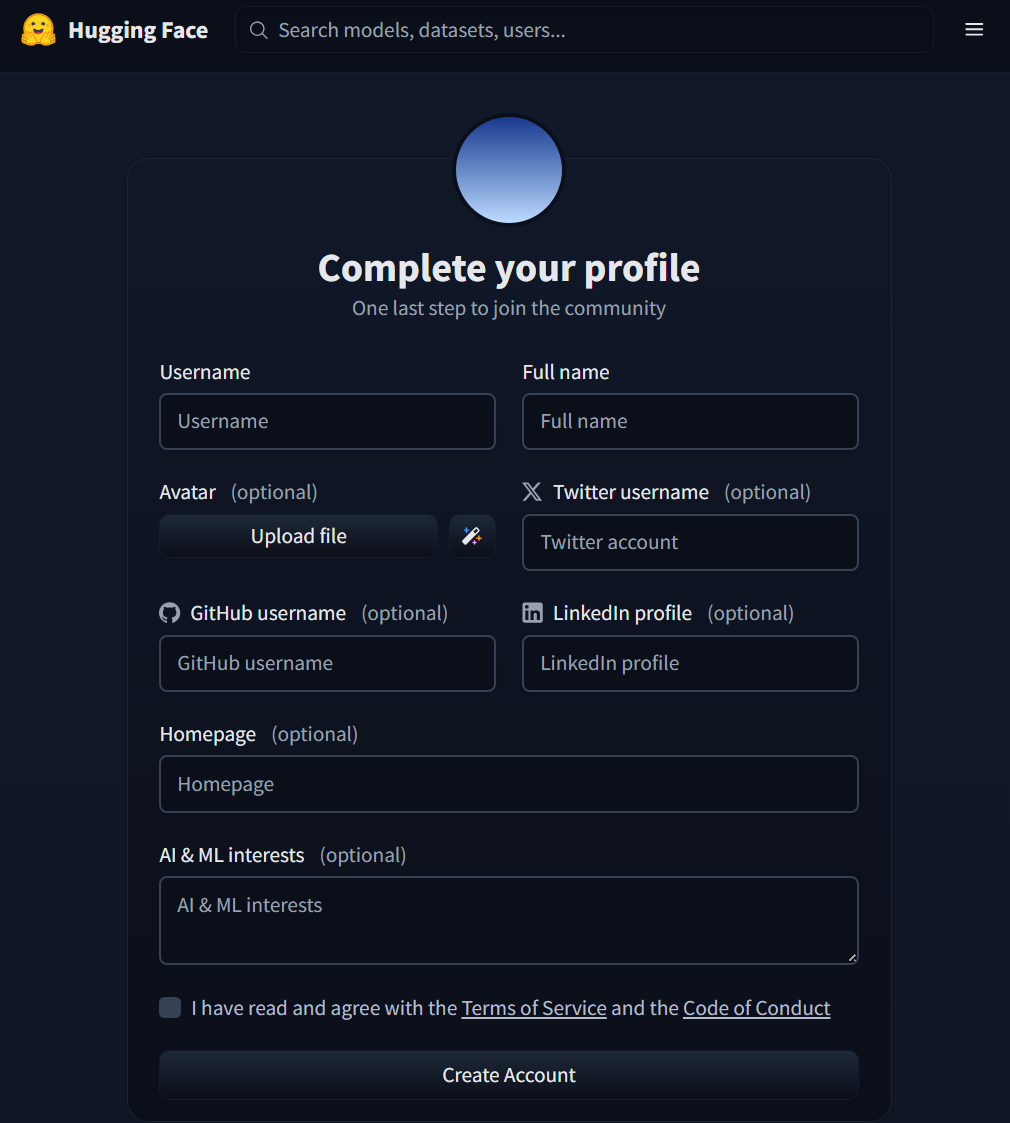
We’ll use a couple of machine learning models that require a quick signup. These models are available on Hugging Face—think of it as a GitHub-style hub for ML—where many models can be used for free for learning and other non-commercial purposes.
If you haven’t seen the previous post, check it out first. We’ll build on that setup and add speaker diarization as a new feature.
Step by step
Assume the environment created last time has the following folder structure.
This time, we will create a folder called models under the venv folder and install a new training model in the models folder. The Python executable we will create last will be designed with this folder structure and a PATH specification. It is important to faithfully create the folder hierarchy.
C:\Users\hoge\Documents\WhisPy\
├─ venv\
├─ web.py
└─ (etc...file,readme.txt)
Installing Git
In the previous step, we installed chocolatey. Install git with the following command. After installation, restart PowerShell or Terminal.
choco install gitHugging Faceへサインアップ
サインアップと必要な設定は次の手順です。
Installing a machine learning model Pyannote.audio
Create a folder named models
cd ~\documents\WisPymkdir modelsIn the terminal, navigate to the models folder.
cd ~\documents\WispPy\modelsThen run two commands
git lfs installgit clone https://hf.co/pyannote/speaker-diarization-community-1 ./pyannote-speaker-diarization-community-1You will be asked for authentication information.
The git specified in the clone command is Hugging Face's git.
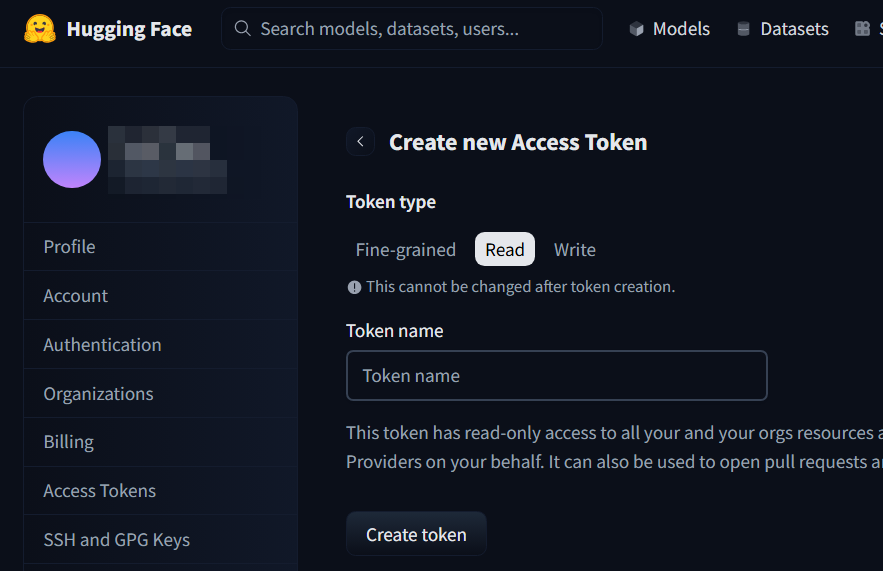
The Username you set in Hugging Face. You can check this on the Settings > Account Information screen in Hugging Face. The Password is the Access Token you created.
Enter this information and click Continue to start cloning.
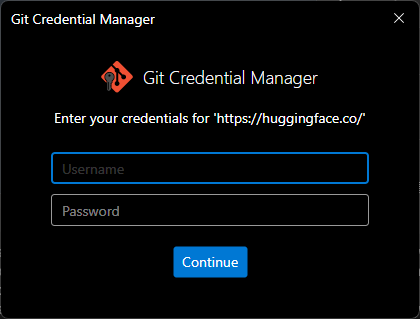
As a side note, git authentication information entered when running Terminal is saved in the Windows Credential Manager. If you view your Windows Credentials in Control Panel > Credential Manager, you should see the following saved information in the list: git:https:\huggingface.co. If incorrect information is saved or you change the token, you can delete it from here and enter it again.
This token is only used when installing the pyannote model. You can delete it after installation.
Create App Py File
venvフォルダ配下に web2.pyを作成し次のコードを保存します。
#!/usr/bin/env python3
"""
Whisper Transcription Web App
(Streamlit, for Windows, settings displayed on main screen, speaker diarization option, fully local model)
"""
import os
import time
import tempfile
from datetime import datetime
import streamlit as st
import torch
import whisper
# ===== Check for pyannote.audio availability =====
try:
from pyannote.audio import Pipeline # type: ignore
HAVE_PYANNOTE = True
except ImportError:
HAVE_PYANNOTE = False
# ===== Check for torchaudio availability (Used to avoid AudioDecoder issues) =====
try:
import torchaudio # type: ignore
HAVE_TORCHAUDIO = True
except ImportError:
HAVE_TORCHAUDIO = False
# ===== Path Settings (Assumes 'models' folder is in the same directory as app.py) =====
BASE_DIR = os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__))
PYANNOTE_MODEL_DIR = os.path.join(
BASE_DIR, "models", "pyannote-speaker-diarization-community-1"
)
# ===== Initialize Session State for result persistence =====
if "transcript_text" not in st.session_state:
st.session_state["transcript_text"] = ""
if "transcript_meta" not in st.session_state:
st.session_state["transcript_meta"] = {}
if "labeled_segments" not in st.session_state:
st.session_state["labeled_segments"] = None
if "last_filename" not in st.session_state:
st.session_state["last_filename"] = ""
# Page Configuration
st.set_page_config(
page_title="Whisper Transcription Tool",
page_icon="🔊",
layout="wide",
)
@st.cache_resource
def load_whisper_model(model_name: str):
"""Load Whisper model (Cached)"""
device = "cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu"
return whisper.load_model(model_name, device=device)
@st.cache_resource
def load_diarization_pipeline():
"""
Load pyannote.audio speaker diarization pipeline (Cached)
Reads the model from a local directory previously git-cloned from Hugging Face.
"""
if not HAVE_PYANNOTE:
raise RuntimeError("pyannote.audio is not installed.")
if not os.path.isdir(PYANNOTE_MODEL_DIR):
raise RuntimeError(
"pyannote model directory not found.\n"
f"Expected path: {PYANNOTE_MODEL_DIR}\n"
"Please clone it into the models folder within your venv as follows:\n"
" git lfs install\n"
" git clone https://huggingface.co/pyannote/speaker-diarization-community-1 "
"models/pyannote-speaker-diarization-community-1"
)
pipeline = Pipeline.from_pretrained(PYANNOTE_MODEL_DIR)
if torch.cuda.is_available():
pipeline.to(torch.device("cuda"))
return pipeline
def check_ffmpeg():
"""Verify if FFmpeg is installed (using NUL for Windows)"""
if os.system("ffmpeg -version > NUL 2>&1") != 0:
st.error(
"⚠️ FFmpeg is not installed.\n"
" Example: Run `choco install ffmpeg` in PowerShell with Administrator privileges, \n"
" then restart your terminal and try again. (Example for Chocolatey users)."
)
st.stop()
def get_available_models():
"""List of selectable Whisper models"""
return ["tiny", "base", "small", "medium", "large"]
def format_timestamp(seconds: float) -> str:
"""Convert seconds to H:MM:SS.mmm format"""
dt = datetime.utcfromtimestamp(seconds)
return dt.strftime("%H:%M:%S.%f")[:-3]
def attach_speakers_to_whisper_segments(segments, diarization):
"""
Simple implementation to assign speaker labels to Whisper segments.
- Determines the speaker based on which pyannote segment contains
the "midpoint time" of each Whisper segment.
"""
labeled = []
# Support for both pyannote.audio 4.x DiarizeOutput and 3.x Annotation
if hasattr(diarization, "speaker_diarization"):
annotation = diarization.speaker_diarization
else:
annotation = diarization
diar_segments = []
for turn, _, speaker in annotation.itertracks(yield_label=True):
diar_segments.append(
{
"start": float(turn.start),
"end": float(turn.end),
"speaker": str(speaker),
}
)
for seg in segments:
start = float(seg["start"])
end = float(seg["end"])
mid = 0.5 * (start + end)
speaker_label = "UNKNOWN"
for ds in diar_segments:
if ds["start"] <= mid <= ds["end"]:
speaker_label = ds["speaker"]
break
new_seg = dict(seg)
new_seg["speaker"] = speaker_label
labeled.append(new_seg)
return labeled
def main():
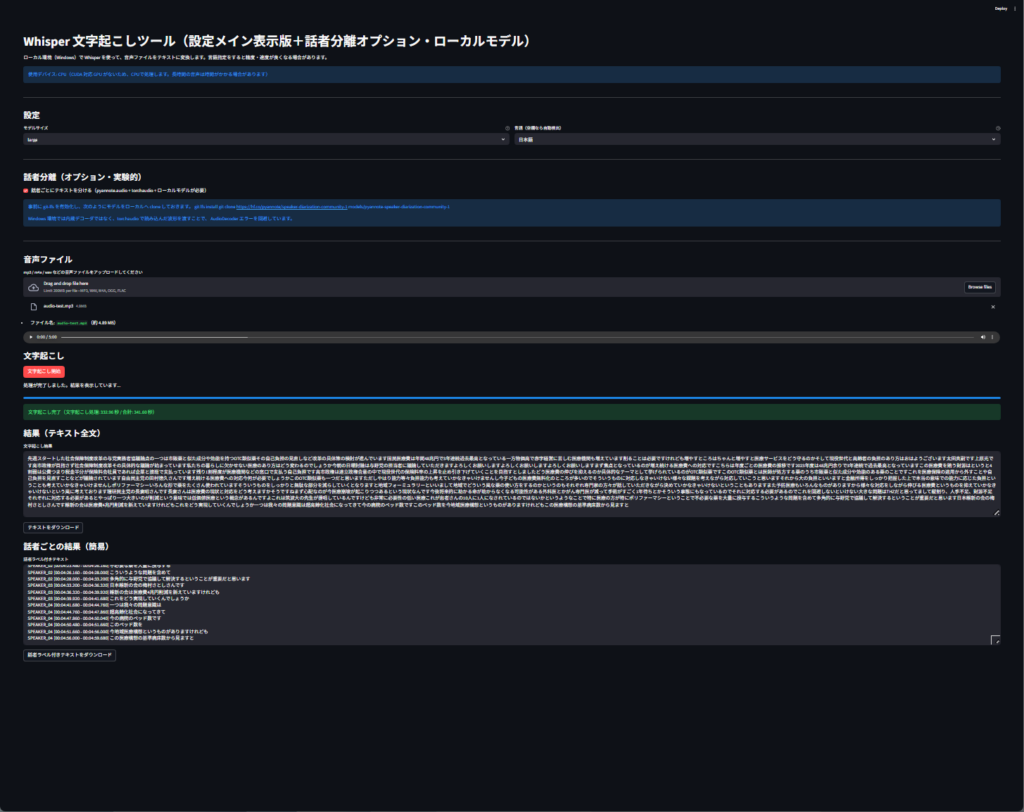
st.title("Whisper Transcription Tool (Settings Main + Diarization Option, Local Model)")
st.write(
"Convert audio files to text using Whisper in a local Windows environment. "
"Specifying the language can improve accuracy and speed."
)
# Check for FFmpeg
check_ffmpeg()
# Device Info
if torch.cuda.is_available():
device_label = "GPU (CUDA)"
st.info(f"Device in use: {device_label}")
else:
device_label = "CPU"
st.info(
f"Device in use: {device_label} (Processing on CPU due to no CUDA-compatible GPU. "
"Longer audio may take more time.)"
)
st.markdown("---")
# ===== Settings Area =====
st.subheader("Settings")
col1, col2 = st.columns(2)
with col1:
model_name = st.selectbox(
"Model Size",
options=get_available_models(),
index=1, # Default to 'base'
help="Larger models improve accuracy but increase processing time and memory usage.",
)
with col2:
language_code = st.selectbox(
"Language (Auto-detect if blank)",
options=["", "en", "ja", "zh", "de", "fr", "es", "ko", "ru"],
index=0,
format_func=lambda x: {
"": "Auto-detect",
"en": "English",
"ja": "Japanese",
"zh": "Chinese",
"de": "German",
"fr": "French",
"es": "Spanish",
"ko": "Korean",
"ru": "Russian",
}.get(x, x),
help="Specifying the audio language leads to more stable accuracy and speed.",
)
# ===== Speaker Diarization Option =====
st.markdown("---")
st.subheader("Speaker Diarization (Optional / Experimental)")
use_diarization = st.checkbox(
"Separate text by speaker (Requires pyannote.audio + torchaudio + local model)",
value=False,
)
if use_diarization:
if not HAVE_PYANNOTE:
st.error(
"pyannote.audio is not installed.\n"
" Example: Run `pip install pyannote.audio` within your virtual environment."
)
if not HAVE_TORCHAUDIO:
st.error(
"torchaudio is not installed.\n"
" Example: Run `pip install torchaudio` within your virtual environment."
)
st.info(
"Enable git-lfs and clone the model locally beforehand:\n"
" git lfs install\n"
" git clone https://huggingface.co/pyannote/speaker-diarization-community-1\n"
" models/pyannote-speaker-diarization-community-1\n\n"
"In Windows, we avoid AudioDecoder errors by passing the waveform loaded via torchaudio "
"instead of the built-in decoder."
)
st.markdown("---")
# ===== Audio File Upload =====
st.subheader("Audio File")
uploaded_file = st.file_uploader(
"Upload audio files such as mp3 / m4a / wav",
type=["mp3", "wav", "m4a", "ogg", "flac"],
)
if uploaded_file is None:
st.info("Upload an audio file to see information here.")
else:
ext = uploaded_file.name.split(".")[-1].lower()
file_size_mb = uploaded_file.size / (1024 * 1024)
st.write(f"- Filename: `{uploaded_file.name}` (approx. {file_size_mb:.2f} MB)")
st.audio(uploaded_file, format=f"audio/{ext}")
st.session_state["last_filename"] = uploaded_file.name
st.markdown("### Transcription")
# ===== Run processing only when the button is clicked, store results in session_state =====
if uploaded_file is not None and st.button("Start Transcription", type="primary"):
progress_text = st.empty()
progress_bar = st.progress(0)
try:
diarization_result = None
labeled_segments = None
# 1. Create temporary file
progress_text.text("Creating temporary file...")
progress_bar.progress(10)
with tempfile.NamedTemporaryFile(delete=False, suffix=f".{ext}") as tmp:
tmp.write(uploaded_file.getvalue())
temp_path = tmp.name
# 2. Load Whisper model
progress_text.text(f"Loading Whisper model `{model_name}`...")
load_start = time.time()
model = load_whisper_model(model_name)
load_end = time.time()
progress_bar.progress(40)
progress_text.text(
f"Model loaded ({load_end - load_start:.2f}s). Starting transcription..."
)
# 3. Transcribe with Whisper
transcribe_start = time.time()
progress_bar.progress(50)
transcribe_options = {}
if language_code:
transcribe_options["language"] = language_code
result = model.transcribe(temp_path, **transcribe_options)
transcribe_end = time.time()
progress_bar.progress(80)
progress_text.text("Transcription complete. Performing speaker diarization if applicable...")
total_time = transcribe_end - load_start
transcribe_time = transcribe_end - transcribe_start
# 4. Speaker Diarization (Optional/Local Model)
if use_diarization and HAVE_PYANNOTE and HAVE_TORCHAUDIO:
try:
progress_text.text("Running speaker diarization (pyannote.audio + torchaudio)...")
diar_start = time.time()
pipeline = load_diarization_pipeline()
waveform, sr = torchaudio.load(temp_path)
diarization_result = pipeline(
{"waveform": waveform, "sample_rate": sr}
)
diar_end = time.time()
progress_bar.progress(95)
progress_text.text(
f"Diarization complete (approx. {diar_end - diar_start:.2f}s). Merging results..."
)
segments = result.get("segments", [])
if segments:
labeled_segments = attach_speakers_to_whisper_segments(
segments, diarization_result
)
except Exception as e:
st.warning(
"An error occurred during speaker diarization.\n"
"Skipping diarization and displaying standard transcription only.\n"
f"Details: {e}"
)
progress_bar.progress(100)
progress_text.text("Processing complete. Displaying results...")
# ===== Store results in session_state =====
text = result.get("text", "") or ""
st.session_state["transcript_text"] = text
st.session_state["transcript_meta"] = {
"transcribe_time": transcribe_time,
"total_time": total_time,
}
st.session_state["labeled_segments"] = labeled_segments
st.success(
f"Transcription Complete (Transcription: {transcribe_time:.2f}s / Total: {total_time:.2f}s)"
)
except Exception as e:
progress_bar.progress(0)
progress_text.empty()
st.error(f"An error occurred: {e}")
finally:
if "temp_path" in locals() and os.path.exists(temp_path):
try:
os.unlink(temp_path)
except OSError:
pass
# ===== Display results stored in session_state =====
meta = st.session_state.get("transcript_meta", {})
transcript_text = st.session_state.get("transcript_text", "")
labeled_segments = st.session_state.get("labeled_segments", None)
last_filename = st.session_state.get("last_filename", "result")
if transcript_text:
# Display meta info if available
if meta:
st.info(
f"Previous transcription result (Processing time: "
f"{meta.get('transcribe_time', 0):.2f}s / "
f"Total: {meta.get('total_time', 0):.2f}s)"
)
st.markdown("### Result (Full Text)")
st.text_area(
"Transcription Result",
value=transcript_text,
height=250,
key="full_text_area",
)
st.download_button(
label="Download Text",
data=transcript_text,
file_name=f"{os.path.splitext(last_filename)[0]}_transcript.txt",
mime="text/plain",
key="download_full_text",
)
# ===== Display Speaker Diarization Results =====
if labeled_segments:
st.markdown("### Results by Speaker (Summary)")
speaker_lines = []
for seg in labeled_segments:
spk = seg.get("speaker", "UNKNOWN")
start_ts = format_timestamp(float(seg["start"]))
end_ts = format_timestamp(float(seg["end"]))
seg_text = seg.get("text", "").strip()
line = f"{spk} [{start_ts} - {end_ts}] {seg_text}"
speaker_lines.append(line)
speaker_text = "\n".join(speaker_lines)
st.text_area(
"Text with Speaker Labels",
value=speaker_text,
height=300,
key="speaker_text_area",
)
st.download_button(
label="Download Text with Speaker Labels",
data=speaker_text,
file_name=f"{os.path.splitext(last_filename)[0]}_speaker.txt",
mime="text/plain",
key="download_speaker_text",
)
elif use_diarization and not HAVE_PYANNOTE:
st.warning(
"Speaker diarization was not executed because pyannote.audio is not installed."
)
elif use_diarization and not HAVE_TORCHAUDIO:
st.warning(
"Speaker diarization was not executed because torchaudio is not installed."
)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()ad
Test Check
This is a sample result. Since my GPU was not supported, the calculation appears to be performed CPU-only. A 5-minute, 1700-character, 100-line audio file took approximately 2 minutes and 30 seconds. The Whisper model details were measured using the base version.
ad